Learning Mode (Active Monitoring)
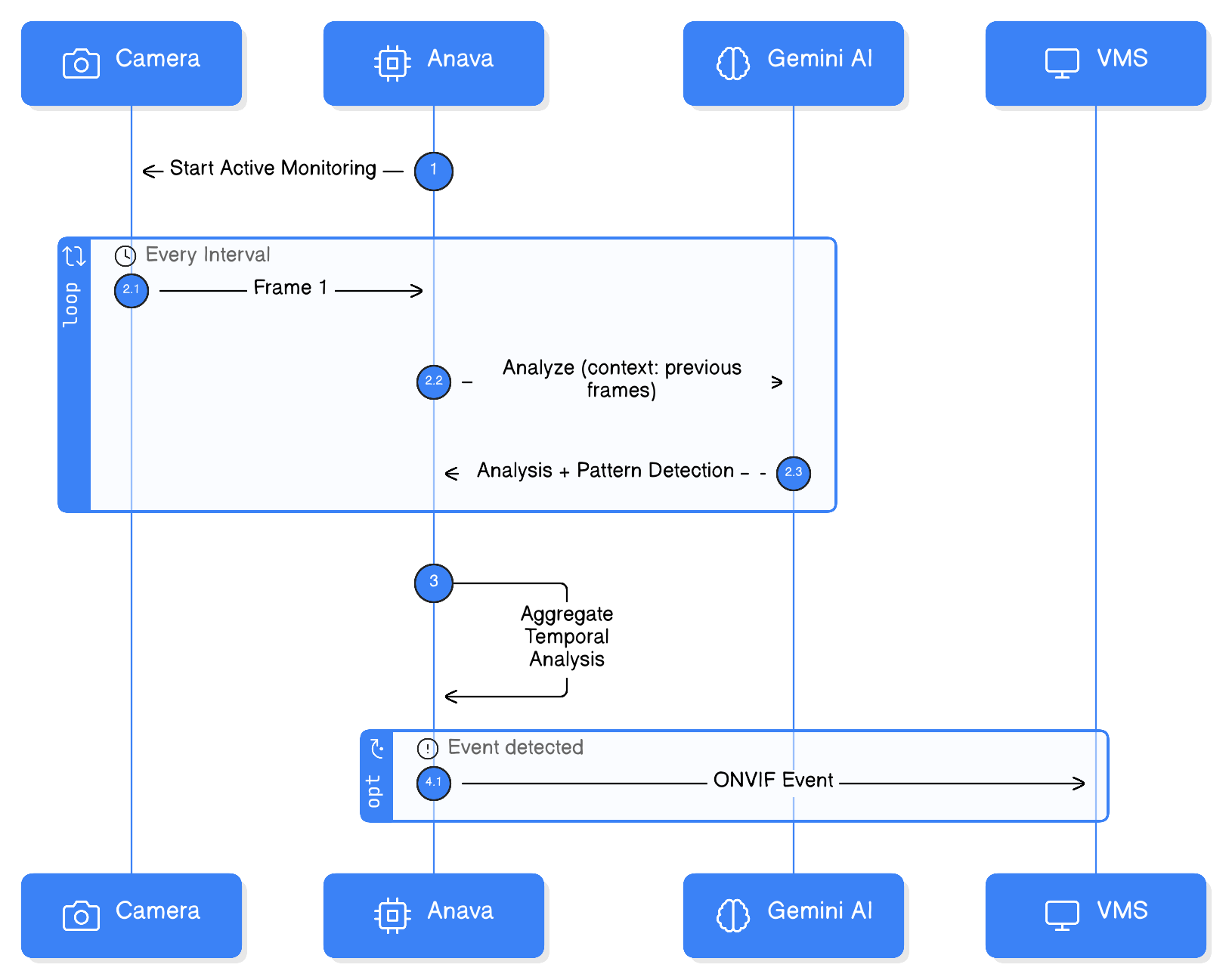
Learning Mode, also called Active Monitoring, enables continuous frame capture and temporal analysis. This allows detection of behaviors that unfold over time, like loitering, crowd formation, or process compliance.
What is Learning Mode?
Unlike trigger-based analysis (single frame when event occurs), Learning Mode:
- Captures multiple frames over time
- Analyzes patterns and changes
- Detects behaviors, not just objects
Use Cases
| Behavior | Description | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Loitering | Person in area too long | 60s duration, 10s interval |
| Crowd Formation | People gathering over time | 120s duration, 15s interval |
| Queue Growth | Line getting longer | 300s duration, 30s interval |
| Abandonment | Object left behind | 120s duration, 20s interval |
| Process Compliance | Steps followed correctly | 180s duration, 10s interval |
Configuration
Profile Settings
Enable Active Monitoring in your profile:
| Setting | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn on continuous capture | true/false |
| Interval (ms) | Time between captures | 1000-60000 |
| Max Duration (sec) | Total monitoring window | 30-600 |
| Max Images | Total images to capture | 5-50 |
| Batch Size | Frames sent together | 1-10 |
| Resolution | Image quality | TINY to ULTRA |
Example: Loitering Detection
Profile: Loitering Alert
Trigger: AOAS Person (to start monitoring)
Active Monitoring:
Enabled: true
Interval: 10000 # Every 10 seconds
Max Duration: 60 # Watch for 1 minute
Max Images: 6 # 6 frames total
Batch Size: 3 # Send 3 at a time
Resolution: BALANCED
Skill:
Prompt: "Track this person over multiple frames. Determine if
they are loitering (remaining in approximately the same
area) or moving through the scene."
Objects:
- Loitering (bool, stateful)
Example: Crowd Monitoring
Profile: Crowd Formation Alert
Trigger: Schedule (every 5 minutes)
Active Monitoring:
Enabled: true
Interval: 15000 # Every 15 seconds
Max Duration: 120 # 2 minute window
Max Images: 8
Batch Size: 2
Resolution: LOW
Skill:
Prompt: "Monitor crowd density over time. Alert if crowd
size is growing or exceeds safe capacity."
Questions:
- "Current count?" (int)
- "Trend?" (string: growing/stable/shrinking)
- "Capacity concern?" (bool)
Trigger Strategies
Schedule Trigger (Continuous)
Poll at regular intervals:
- Use when: Continuous monitoring needed
- Trigger: Schedule
- Interval: Minutes between polls
Example: Queue monitoring every 2 minutes
Event Trigger (On Demand)
Start monitoring when something happens:
- Use when: Resource-efficient monitoring
- Trigger: AOAS Person, Motion, or I/O
- Active Monitoring starts on trigger
Example: Start loitering watch when person detected
Hybrid Approach
Combine both strategies:
- Schedule polls for baseline monitoring
- Event triggers for focused attention
Temporal Prompts
Prompt Design for Temporal Analysis
Include temporal context in prompts:
Standard Prompt:
Analyze this image for security concerns.
Temporal Prompt:
You are seeing multiple frames over a 60-second period.
Analyze for:
1. Is the same person present across frames?
2. Are they stationary (loitering) or moving through?
3. Have they made any concerning movements?
4. Compare the first and last frames - what changed?
Frame Referencing
Anava provides temporal context to the AI:
- Frame sequence information
- Time elapsed
- Previous analysis results
The AI can reference:
- "In the first frame..."
- "Compared to earlier..."
- "Over the monitoring period..."
Performance Optimization
Resource Usage
Active Monitoring uses more resources than single-frame analysis:
| Setting | Resource Impact |
|---|---|
| Shorter interval | More frames, higher cost |
| Longer duration | More data to analyze |
| Higher resolution | More bandwidth, storage |
| Larger batch | More memory per analysis |
Recommended Configurations
| Use Case | Interval | Duration | Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loitering | 10s | 60s | 6 |
| Crowd trend | 15s | 120s | 8 |
| Queue length | 30s | 300s | 10 |
| Process step | 5s | 60s | 12 |
Reducing False Positives
For temporal analysis:
- Require pattern across multiple frames
- Use confirmation in prompts ("Must see in 3+ frames")
- Set appropriate duration for the behavior
VMS Integration
ONVIF Events from Active Monitoring
Events emit when:
- Behavior is confirmed across frames
- Threshold is met (e.g., loitering > 45 seconds)
- Pattern detected (e.g., crowd growing)
Event Timing
| Event Type | When Emitted |
|---|---|
| Detection | When behavior confirmed |
| Clear | When behavior ends or duration expires |
| Update | (Optional) As confidence increases |
VMS Action Rules
Configure VMS to respond to temporal events:
- Loitering detected → Start high-quality recording
- Crowd alert → Notify operations
- Process violation → Log and alert
Troubleshooting
Monitoring Not Starting
-
Check trigger is firing
- Verify event reaches ACAP
- Check profile is active
-
Check configuration
- Enabled = true
- Valid interval/duration
-
Check camera connection
- Device online
- MQTT connected
Inconsistent Detection
-
Frame quality
- Increase resolution if details needed
- Check lighting conditions
-
Interval too long
- May miss quick behaviors
- Shorten for rapid changes
-
Duration too short
- Behavior needs more time to establish
- Extend for slower patterns
High False Positives
-
Require confirmation
- Must detect in multiple frames
- Add to prompt requirements
-
Adjust threshold
- Higher confidence for events
- Lower for logging only
Best Practices
Match Duration to Behavior
| Behavior | Typical Duration |
|---|---|
| Quick check | 30s |
| Loitering | 60-120s |
| Crowd forming | 120-300s |
| Process steps | Varies by process |
Balance Resources
- Start with longer intervals, shorter durations
- Adjust based on detection needs
- Monitor costs and adjust
Document Configuration
Keep records of:
- Active Monitoring settings
- Detection goals
- False positive rates
- Adjustments made
Related Topics
- Tuning & Optimization - Overall tuning strategies
- Profiles Reference - Profile configuration
- Event Flow - Understanding analysis pipeline